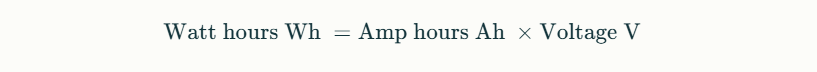Amp-Hours to Watt-Hours Conversion
Understanding the conversion between amp-hours (Ah) and watt-hours (Wh) is crucial for accurately assessing battery capacity across different voltage systems. The formula for this conversion is straightforward: watt-hours equal amp-hours multiplied by voltage.
| Voltage | Capacity (Ah) | Energy Storage (Wh) |
|---|---|---|
| 12V | 100Ah | 1,200Wh |
| 24V | 100Ah | 2,400Wh |
| 48V | 100Ah | 4,800Wh |
This table illustrates how the same 100Ah capacity translates to different energy storage capabilities depending on the system voltage. For instance, a 12V 100Ah battery stores 1,200Wh of energy, while a 48V 100Ah battery provides a substantial 4,800Wh. This conversion is essential for comparing batteries across various applications and determining the most suitable power solution for specific energy requirements.
To convert 100 amp-hours (Ah) of lithium battery capacity into watt-hours (Wh) or kilowatt-hours (kWh), you need to know the voltage (V) of the battery, as the relationship between these units is given by the formula:
12V Battery Scenario
A 12V 100Ah lithium battery is a common configuration in various applications, offering a balance of portability and power. This setup provides 1,200 watt-hours of energy, making it suitable for many small to medium-sized power needs.
| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Voltage | 12V |
| Capacity | 100Ah |
| Energy Storage | 1,200Wh |
This battery configuration is widely used in recreational vehicles, marine applications, and small off-grid solar systems. It’s particularly advantageous for its compatibility with many 12V appliances and devices. Under ideal conditions, a 12V 100Ah lithium battery paired with a 1000W inverter can provide power for approximately 1.2 hours, though actual runtime may vary depending on the depth of discharge and system efficiency.
24V Battery Scenario
The 24V lithium battery configuration with a 100Ah capacity offers a middle ground between the 12V and 48V systems, providing enhanced power capabilities while maintaining versatility. This setup delivers 2,400 watt-hours of energy, striking a balance between voltage and storage capacity.
| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Voltage | 24V |
| Capacity | 100Ah |
| Energy Storage | 2,400Wh |
24V systems are commonly used in medium-sized solar installations, electric boats, and some industrial applications. They offer improved efficiency over 12V systems, reducing power loss in cables and allowing for the use of smaller gauge wiring. This configuration is particularly suitable for applications that require more power than a 12V system can efficiently provide, but don’t necessarily need the high voltage of a 48V setup. The 24V 100Ah lithium battery’s increased energy density makes it an excellent choice for applications where space and weight are considerations, while still offering significant power output for a wide range of devices and equipment.
48V Battery Scenario
The 48V 100Ah lithium battery configuration represents a high-power solution, offering significant energy storage capacity and improved efficiency for larger-scale applications. This setup provides an impressive 4,800 watt-hours of energy, making it ideal for demanding power needs.
| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Voltage | 48V |
| Capacity | 100Ah |
| Energy Storage | 4,800Wh |
48V systems are commonly used in large off-grid solar installations, electric vehicles, and industrial equipment. They offer superior efficiency compared to lower voltage systems, allowing for reduced current flow and minimized power loss over long distances. This configuration is particularly advantageous for high-power applications that require sustained energy output, such as powering multiple appliances simultaneously or supporting energy-intensive industrial processes. The 48V 100Ah lithium battery’s high energy density makes it an excellent choice for applications where maximizing power output within space constraints is crucial, providing a robust and versatile power solution for a wide range of advanced energy needs.
recommended reading
Conclusion
In conclusion, the equivalence of a 100Ah lithium battery varies significantly based on the system voltage. A 12V 100Ah lithium battery provides 1,200Wh, a 24V system offers 2,400Wh, while a 48V configuration delivers an impressive 4,800Wh of energy storage. This scalability demonstrates the versatility of lithium batteries across different applications, from small portable devices to large-scale industrial systems. Lithium batteries, particularly lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), offer superior performance compared to traditional lead-acid batteries, with higher energy density, longer cycle life, and better efficiency. When selecting a battery system, it’s crucial to consider factors such as voltage requirements, energy needs, and specific application demands to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Learn How RAKOUR Can help you deploy
future-proof energy
Our team of energy storage experts will take the time to fully understand your business, challenges , and opportunities.

What is a LiFePO4 Battery? A LiFePO4 battery, or Lithium Iron Phosphate battery, is a

Exploring Lifepo4 Lithium Battery for Solar Applications
Lifepo4 lithium battery are becoming the preferred choice for solar applications due to their superior

Li ion Battery vs. Lithium Phosphate: Key Differences
The debate between li-ion battery technology and lithium phosphate batteries is crucial for various applications,

What is the full charge of LiFePO4 48V battery?
LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) 48V batteries are integral to numerous applications, with their voltage levels

How long does a 12 volt deep cycle marine battery last
The lifespan of a 12-volt deep cycle marine battery is influenced by various factors, including
What is LFP Battery? Features and Benefits
What is an LFP battery? LFP, or lithium iron phosphate battery, is a type of
FAQs